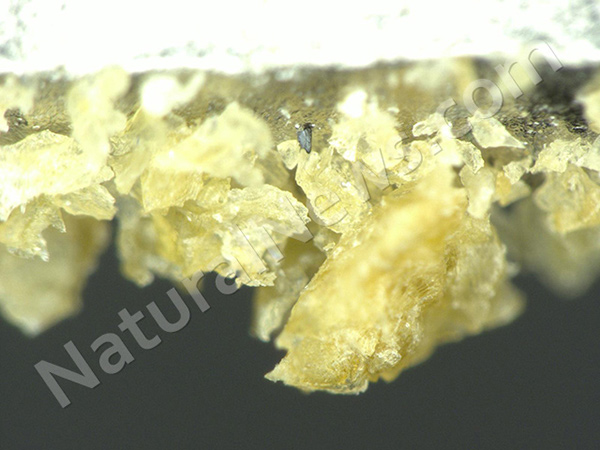
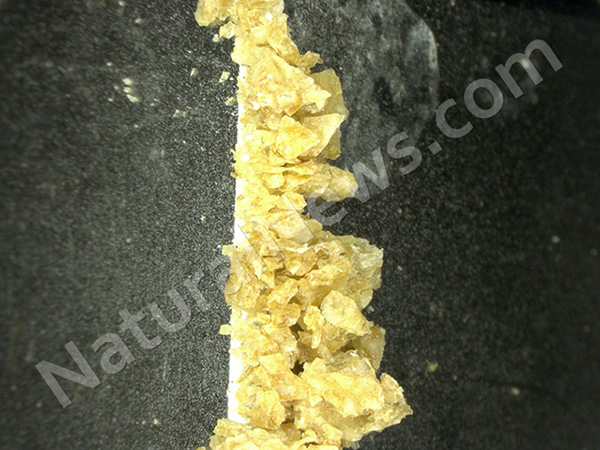
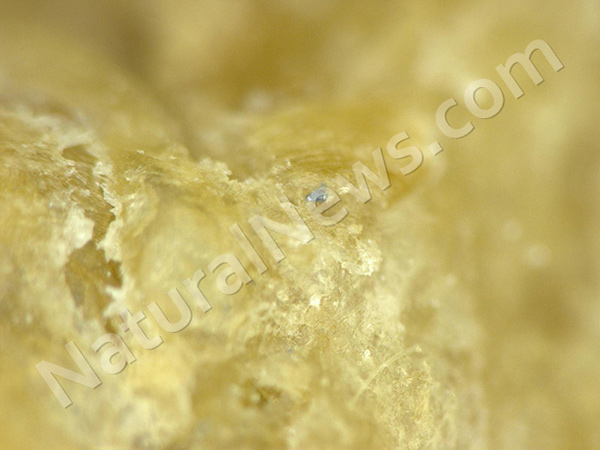
WARNING: On top of the GMO high fructose corn syrup,
the ingredients inside this imitation fruit beverage pose the risk of forming a known carcinogen inside the bottle – just waiting for you to drink it.
It’s been more than 20 years since the FDA and beverage industry first learned that sodium benzoate and citric acid or ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) can create the carcinogen benzene while in the bottle together. The public was informed just seven years ago, and yet, many makers of artificial fruit drinks and sodas still frequently (and shamefully) use these ingredients in this risky combination on the market today, or with variant formulas like potassium benzoate, which has the same effect.
The soda companies and the FDA knew back in the early 1990s; the public didn’t find out until it made headlines in 2006 that these ingredients were creating a public health hazard no one wanted to address.
Supporting evidence:
From the American Chemical Society in 1993 – Benzene production from decarboxylation of benzoic acid in the presence of ascorbic acid and a transition-metal catalyst
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf00029a001
From 2008 Belgian study – Benzene formation from Sodium/Potassium Benzoate and Citric Acid is worsened by plastic bottle packaging
http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jf072580q
2008: Diet Coke to drop additive in DNA damage fear
http://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-1021820/Diet-Coke-drop-additive-DNA-damage-fear.html
Meanwhile, the same ingredient – added to your food as a preservative – also poses another admitted risk: the 40 year old thesis that artificial color dyes & additives – including sodium benzoate – were making kids hyperactive and/or ADHD and irritating allergies was officially confirmed and publicly recognized, prompting EU bans, in the 2007 Southampton study.
Supporting evidence:
Sodium Benzoate, Artificial Colors & ADHD/Hyperactivity in Children: Key Southampton Study from 2007 – Food additives and hyperactive behaviour in 3-year-old and 8/9-year-old children in the community: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled trial
http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140673607613063/abstract
Artificial Food Colorings & Benzoate Preservative, from 2004: The effects of a double blind, placebo controlled, artificial food colourings and benzoate preservative challenge on hyperactivity in a general population sample of preschool children
http://adc.bmj.com/content/89/6/506.short
This artificial beverage – one of the least enlightened products anywhere on store shelves, and marketed directly to Hispanics already at a higher risk for food-derived health decline – not only gives its customer base the literal formula for creating benzene, a known toxin, inside the bottle [sodium benzoate + citric acid + ascorbic acid (Vitamin C extract likely derived from corn)], but it also provides consumers with every opportunity for hyperactivity with ingredients Yellow #5 & Yellow #6 and sodium benzoate all in one batch, as well as every opportunity for obesity, diabetes, et al. via the ‘contains no juice’ yet filled with loads of high fructose corn syrup approach to refreshment.
With ingredients this good, why not just go into a science lab and guzzle down any random yellow liquid you find?
Further supporting evidence on this complex social issue may help address several concerns with no easy answer (or alternately no easy solution):
• Should oligopolistic cartels control the “free market”?
• Should Michael Bloomberg lead the way in dictatorial nanny state calorie control just because the majority of the food supply is laced with dangerous additives?
• Should U.S. taxpayers be forced to subsidize GMO corn & soy by the billions, along with filthy, toxic CAFO feedlots to produce beef & chicken, etc. et al. and pay Big Agra to effectively poison the population?
SLAVE MARKET FOODS: Studies, and a bit of common sense, show that classifications on the socio-economical scale such as low income, inner city and/or ethnic minority [Hispanic/Black] predisposes consumers (who are equal under the law to protections against harm) to diabetes, obesity and other health risks as grocery stores in their area tend to sell lower qualities foods while food producers price high quality (or even halfway decent) foods out of reach.
Again, the product in this video (above) is a good example, as is this GMO- and artificial ingredient-filled powdered drink mix Truthstream previously covered.
Seriously, there are studies about poor people and the poor food they are all but forced to eat by circumstances.
How can this be right? Obviously, food stamps and the dependent population system is hurting not helping this phenomenon:
Barriers to Buying Healthy Foods for People With Diabetes: Evidence of Environmental Disparities
http://ajph.aphapublications.org/doi/abs/10.2105/AJPH.94.9.1549
Poverty and obesity: the role of energy density and energy costs
http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/79/1/6.short
The economics of obesity: dietary energy density and energy cost
http://ajcn.nutrition.org/content/82/1/265S.short
Food Choices and Diet Costs: an Economic Analysis
http://jn.nutrition.org/content/135/4/900.short
Choosing to eat unhealthy junk foods rather then choosing healthy foods and living a healthy lifestyle at the individual level may be important and significant to the outcome of our life’s work, but there is no denying that the system is making a lot of these choices for people without their consent or full knowledge.
The poverty cycle cannot be explained just by irresponsible individuals; clearly many sectors of society are trapped in it, and a market-driven conspiracy to keep them down with shitty food is apparent. Sadly, this is a de facto reality, no matter whether “the elite” have planned it this way, or just failed to correct it…
Planned or not, there are clearly elements of dumbing down the population through diet, essentially social engineering sectors of the population to create a strata of efficient worker bees, subservient functionaries and helpless hoards of jellyfish consumers through targeted metabolisms (just as the queen bee is fed royal jelly all her life, and the drones and workers only get royal jelly in the first days of their lives…) that change the character of people and malnourish thoughts of liberation and creative prosperity.
“Diet, injections, and injunctions will combine, from a very early age, to produce the sort of character and the sort of beliefs that the authorities consider desirable, and any serious criticism of the powers that be will become psychologically impossible. Even if all are miserable, all will believe themselves happy, because the government will tell them that they are so.” – Lord Bertrand Russell, The Impact of Science on Society (1951)
Humans are capable of so much more, but the diet modern society has lived off of will not allow the population to attain this potential. Instead, people are treated as human capital/cattle. Think about it… you are what you eat holds as true as ever!
Source: Truthstream Media